
COMPANY INFORMATION
Risk Management
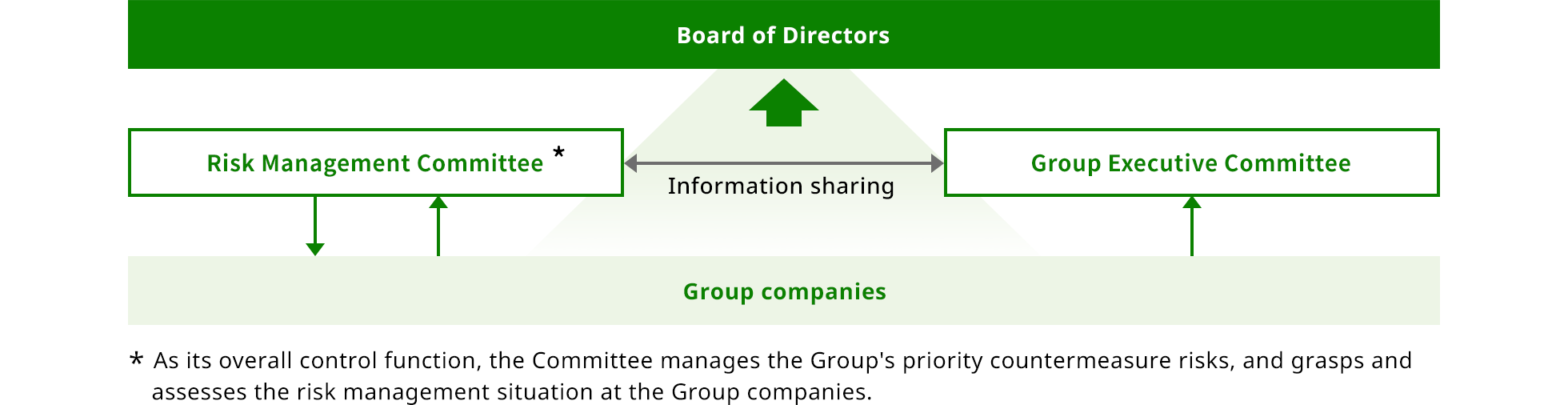
Risk management structure
The Risk Management Committee and the Group Executive Committee each manages respective significant risks according to the types of risk with the Risk Management Committee controlling the overall risk management and reporting to the Board of Directors.
The Risk Management Committee manages the Group’s priority countermeasure risks that are thought to require across-the-Group management and grasps and assesses the risk management situation at the Group companies.
A department with primary responsibility is appointed for the Group’s priority countermeasure risks to operate a thorough PDCA cycle of risk management. Additionally, the Group’s overall risk management structure is strengthened by having the Risk Management Committee grasp and assess the risk management situation at the Group companies.
In addition, the Company verifies the sufficiency of its risk management structure and its risk management operations through internal audits and conducts audits of major risks systematically based on their priority. In case of an urgent risk of a major loss, the Company provides information and makes decisions in accordance with its Emergency Response Basic Provisions to minimize the damage.
Risks that are assumed to have a significant impact on management
In the Basic Regulations on Risk Management, the Group has defined seven individual risks (investment risks, financial and capital risks, personnel and labor risks, legal and compliance risks, IT strategy risks/ digital strategy risks, information security risks and crisis management risks) as events that could interfere with the achievement of management targets of the Group companies. We recognize a significant risk in climate change, which is a risk with high significance.
In addition, the Group has identified opportunities and risks and defined significant risks related to six materialities that the Group has determined in the GROUP VISION 2030.
You can scroll this table sideways
| Materialities | Major opportunities and risks (○ opportunities, ● risks) |
Major fluctuating factors | Significant risks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Create a variety of lifestyles. | ◯Integration of all lifestyle scenes ●Mismatch with consumer needs |
|
Investment risks Financial and capital risks |
| Create well-being communities and lifestyles. | ○Increasing importance of community creation ○Growing needs for disaster readiness and disaster damage reduction ●Subordination in competition between cities ●Decreasing value due to insufficient asset maintenance and management |
||
| Create the sustainable environment. | ○Growing needs to respond to the decarbonized and recycling-oriented society ●Escalation of climate change and natural disasters ●Increasing costs due to stronger environmental restrictions, etc. |
|
Climate change risks |
| Create value in the digital era. | ○Increasing importance of utilizing customer contact points ●Appearance of disruptors to existing businesses |
|
IT strategy risks Digital strategy risks |
| Create an organizational climate under which diverse human capital is enlivened. | ○Emergence of innovation due to diverse human capital ●Intensifying competition in the human capital acquisition market |
|
Personnel and labor risks |
| Create governance to accelerate growth. | ○Strengthening of relationships with stakeholders by improving transparency ●Losses and a decline in confidence due to legal violations and defects in security systems |
|
Information security risks Crisis management risks Legal and compliance risks |
The timing and degree of the possibility that these risks surface and the quantitative details of the impact of these risks on the Group's operating results and financial position, etc. in cases where they do surface are not stated here because it is difficult to reasonably foresee them.
Our view of these risks is as follows.
1.Investment risks
In the Urban Development business and the Strategic Investment business segments, which are asset-utilizing businesses that involve investment among the Group's businesses, tend to be susceptible to factors such as economic trends, corporate earnings, personal consumption trends, real estate market conditions and the competitive environment in Japan and overseas, policy changes by the government and the Bank of Japan, and the situation in business areas, particularly central Tokyo, and these factors could result in a fall in profit margins, a decline in profitability in individual businesses and a fall in the value of assets held.
The Group Corporate Planning Department of the Company is in charge of these risks and manages the risk amount by calculating and continuously monitoring the VaR after defining risks factors for each asset for investment.
2.Financial and capital risks
The Group raises funds for the development of real estate through equity, borrowings from financial institutions and the issuing of bonds. If interest rates rise sharply or if share prices fall markedly in the future, it could have a significant impact on operating results and financial position, etc.
With regard to financing from financial institutions, etc., we work to minimize the impact on operating results in the event of a future rise in interest rates by ensuring that most interest-bearing debt is long-term borrowings and fixing most interest rates for loans other than certain project financing in light of financial conditions to mitigate the impact of fluctuations in interest rates. At the end of the fiscal year ended March 31, 2025, the ratio of long-term borrowings to interest-bearing debt and the ratio of fixed interest rates are 95.3% and 92.4% (both long-term and fixed ratios exclude SPC borrowing), respectively. In addition, the Group Finance Department of the Company is in charge of financing and conducts a trend analysis of the financial market and the quantitative simulation of an impact of rising interest rates on the Company.
In terms of equity, the Group Finance Department conducts a trend analysis of the capital market and provides feedback to the Board of Directors, etc. on the details of dialogues with shareholders and investors in IR activities to continuously ensure the appropriate share price of the Company.
3.Climate change risks
Based on the Environmental Vision established in 1998, the Group is stepping up its environmental initiatives on an ongoing basis through its business activities and recognizes climate change, above all, as an important issue. Transition risks and physical risks in climate change could have an impact on the Group's business. As transition risks, changes in policy trends such as tighter legal regulations including carbon tax, falling demand, and reputational damage to companies that are unable to respond to a low-carbon society are expected. As physical risks, the impact of declining snowfalls due to global warming on the operation of ski resorts and increasing costs due to damage to buildings and longer construction periods caused by the escalation of abnormal weather are expected. These risks could have an adverse impact on business.
The Group Sustainability Promotion Department of the Company is in charge of these risks and deals with them on a Group-wide basis in cooperation with business departments. The Sustainability Committee deliberates and discusses details of initiatives and reports them to the Board of Directors.
In addition, the Company announced its support for the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) recommendations in 2019 and has been participating in the TCFD Consortium, an organization in Japan that discusses TCFD initiatives. Based on the TCFD recommendations, we also implemented disclosures categorized into "Governance," "Strategy," "Risk Management," and "Metrics and Targets". In the fiscal year ended in March2023, we have prepared a "transition plan to a decarbonized society."
[Disclosures based on the TCFD recommendations]
URL: https://tokyu-fudosan-hd-csr.disclosure.site/en/environment/tcfd/
[Transition plan to a decarbonized society]
URL: https://tokyu-fudosan-hd-csr.disclosure.site/en/environment/transition-plan
4.IT strategy risks/ Digital strategy risks
The IT environment surrounding the Group and society is evolving rapidly, and if the Group is unable to respond appropriately and promptly to technological innovations and changes in customer demand, it could have an impact on the Group's operating results and financial position, etc.
The Group IT Strategy Department and the Digital Transformation Promotion Department of the Company are in charge of these risks, and they examine the possibility of application of new technologies to each business.
5.Personnel and labor risks
The Group recognizes diverse personnel as one of its strengths. However, the decline in the working population due to Japan’s low birthrate and aging population, and the resulting labor shortage, could become a major factor hindering the growth of our Group.
In charge of these risks, the Group Human Resources Department of the Company aims to create a company that will be selected by its employees with measures in response to their diverse workstyles, such as telework and the work-from-home system, in addition to the reduction of long working hours and the encouragement of taking paid leave. In addition, the importance of proper labor management is increasing due to the diversification of work styles and working places, and we will implement "proper labor management (proper understanding and management of working hours)" as a Group priority measure starting in fiscal year ended in March 2023. We plan to conduct a comprehensive survey and grasp the status of systems, operations, and awareness-raising activities at each of the companies involved, and report to the Risk Management Committee.
6.Information security risks
The Group handles large volumes of personal information of customers in the Urban Development business, the Property Management & Operation business and the Real Estate Agents business segments. If an information leak occurs due to a cyberattack or the act of a Group employee, it could result in a decline in the social credibility and brand image of the Group and could have an impact on the Group's operating results and financial position, etc.
The Group General Administration Department and the Group IT Strategy Department of the Company are in change of these risks, and they take steps to strengthen security measures and improve the literacy of employees by providing training including an exercise to deal with targeted e-mail attacks.
7.Crisis management risks
If an earthquake, a storm, a flood or any other natural disaster occurs in Japan or overseas, if an act of terrorism, an accident, a fire, an infectious disease or any other human disaster occurs, or if an environmental problem or a defect in real estate is discovered, a dispute could occur in relation to damage to assets held or the fulfillment of compensation obligations, etc., and this could have an impact on the Group's business performance and financial position, etc.
In charge of these risks, the Group General Administration Department of the Company will work to minimize the impact by taking safety measures that will become necessary when a disaster occurs, developing BCP and providing training as preparation for disasters.
8.Legal and compliance risks
If a situation that violates laws and regulations occurs as a result of the Group's employee or business activity, or if the payment of compensation for damages incurred becomes necessary, it could result in a fall in the social credibility and the brand image of the Group and could have an impact on the Group's operating results and financial position, etc.
In charge of these risks, the Group Legal Affairs Department of the Company strives to fully enforce compliance management by building a compliance system at each Group company, including the formulation and promotion of an activity plan (compliance program) to realize compliance. Specifically, the Department strives to make compliance fully known to all officers and employees of the Tokyu Fudosan Holdings Group by establishing the Tokyu Fudosan Holdings Group Code of Conduct that will become the standards of behavior for them, developing the Tokyu Fudosan Holdings Group Compliance Manual as a specific manual to understand and practice the Code of Conduct, and providing training periodically.